What is the HMPV Outbreak All About?
- Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), a respiratory virus similar to the flu, is spreading rapidly in parts of China.
- Vulnerable groups, including children and older adults, are at the highest risk.
- Despite the concerns, health experts emphasize that HMPV is not a new virus and is manageable with proper care and prevention.
Let’s dive into the symptoms, transmission, treatments, and how this virus compares to other respiratory illnesses like COVID-19.

Advertisement:

HMPV Virus in China: What You Need to Know About the Rising Cases
Table of Contents
Introduction
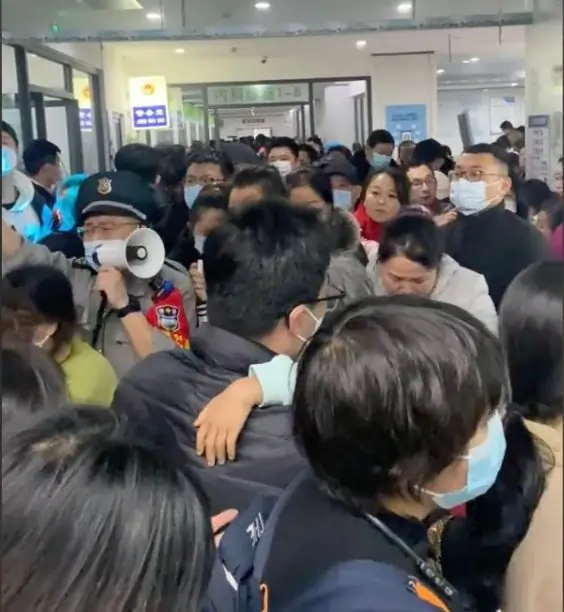
China is currently experiencing a surge in cases of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), raising concerns about a potential new health crisis. Following the COVID-19 pandemic, reports of overwhelmed hospitals and rising respiratory infections have sparked widespread discussions, especially on social media. While authorities have not declared an emergency, the increasing cases of HMPV highlight the need for vigilance and public awareness.
What is HMPV?
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) was first discovered in 2001. Belonging to the Pneumoviridae family, it is closely related to the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). HMPV causes respiratory infections that range from mild flu-like symptoms to severe complications.
Key Facts About HMPV:
- First Identified: 2001 in the Netherlands.
- Who It Affects: All age groups, with young children, older adults, and immunocompromised individuals being most at risk.
- Transmission: Spreads via respiratory droplets, direct contact, or contaminated surfaces.
Symptoms of HMPV
HMPV presents a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
Mild Symptoms:
- Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Fever
- Sore throat
Severe Symptoms:
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Asthma exacerbations
| Symptom Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Mild | Cough, fever, runny nose |
| Severe | Wheezing, pneumonia, bronchitis |
Who Is Most at Risk?
Certain groups are more vulnerable to severe HMPV infections:
- Children under 5 years old, particularly infants.
- Older adults, especially those over 65.
- Individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Patients with chronic respiratory conditions such as asthma or COPD.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads similarly to other respiratory viruses, making it highly contagious during peak seasons.
Transmission Methods:
- Respiratory Droplets: Released through coughing or sneezing.
- Close Contact: Direct contact, such as shaking hands.
- Contaminated Surfaces: Virus-laden surfaces touched and followed by touching the face.
Seasonal Patterns:
HMPV infections typically occur in late winter and spring, aligning with flu season.
Testing and Diagnosis
Testing for HMPV is not always routine but can be done during outbreaks or severe cases.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT): Detects viral genome directly.
- Immunofluorescence or Enzyme Immunoassay: Identifies viral antigens in respiratory secretions.
Treatment Options
There is no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV. Current management focuses on relieving symptoms.
How to Manage HMPV:
- Stay Hydrated and Rest: Essential for recovery.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: For fever, congestion, and pain relief.
- Severe Cases: May require hospitalization for oxygen therapy or intravenous fluids.
Prevention Tips
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers guidelines to minimize the risk of HMPV infections:
- Wash Hands: Use soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid Face Touching: Especially with unwashed hands.
- Wear Masks: In crowded areas or during outbreaks.
- Stay Home: Prevent spreading the virus if sick.
- Disinfect Surfaces: Clean frequently touched objects regularly.
| Prevention Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Handwashing | Use soap and water for 20 seconds. |
| Mask-Wearing | Wear masks in crowded places. |
| Surface Cleaning | Disinfect commonly touched areas. |
Current Situation in China
- Reports of Outbreak: Videos and social media posts show overwhelmed hospitals in northern provinces, where HMPV cases are on the rise.
- Co-Infections: Alongside HMPV, cases of Influenza A, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and COVID-19 have been reported.
- Official Stance: Chinese authorities emphasize that the situation is under control and not a cause for alarm.
How HMPV Compares to COVID-19
HMPV shares similarities with COVID-19 in terms of symptoms and transmission but differs in seasonality and impact.
| Aspect | HMPV | COVID-19 |
|---|---|---|
| Seasonality | Peaks in winter and spring. | Can spread year-round. |
| Transmission | Respiratory droplets, surfaces. | Includes airborne transmission. |
| Variants | Relatively stable. | Continuously evolving. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
According to the Cleveland Clinic, you should consult a healthcare provider if symptoms:
- Worsen after a few days.
- Include difficulty breathing or cyanosis (bluish skin).
- Occur alongside chronic conditions like asthma or COPD.
FAQs
1. What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
HMPV is a respiratory virus that causes flu-like symptoms and can lead to severe complications in vulnerable individuals.
2. How does HMPV spread?
It spreads through respiratory droplets, direct contact, and contaminated surfaces.
3. Is there a vaccine for HMPV?
No, there is currently no vaccine for HMPV. Preventive measures and symptom management are key.
4. How does HMPV compare to COVID-19?
Both cause respiratory symptoms, but HMPV is seasonal, whereas COVID-19 can spread year-round due to evolving variants.
5. What should I do if I suspect HMPV?
Seek medical advice if symptoms worsen, especially if you have difficulty breathing or underlying health conditions.
Conclusion
The surge in HMPV cases in China highlights the importance of vigilance and preventive measures. While it is not an imminent pandemic threat, understanding the virus, its symptoms, and how to prevent its spread is crucial.
Stay informed, practice good hygiene, and consult healthcare professionals when needed.
Disclaimer
The content provided by PinoyTrending is for informational purposes only and is based on publicly available data from reliable sources.
PinoyTrending does not claim sole ownership of this information. Readers are encouraged to consult medical professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment. This article is not a substitute for professional advice and should not be relied upon for decision-making regarding personal health or medical care.
References
- Reuters. “Respiratory Virus Trends in China: HMPV Cases Rising.” Accessed at: https://www.reuters.com/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). “Human Metapneumovirus.” Accessed at: https://www.cdc.gov/
- Cleveland Clinic. “Human Metapneumovirus: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment.” Accessed at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/
- World Health Organization (WHO). “Guidance on Respiratory Illnesses.” Accessed at: https://www.who.int/
- NDTV. “HMPV Virus Cases Surge After COVID-19 Restrictions Eased.” Accessed at: https://www.ndtv.com/
Josh is a seasoned content writer and journalist with over 15 years of experience creating impactful, accurate, and engaging content across industries like technology, healthcare, finance, and media. He specializes in translating complex topics into clear, accessible narratives and excels in technical documentation, editorial writing, and marketing materials.
A skilled journalist, Josh delivers in-depth features and articles that resonate with readers. Known for his attention to detail, research skills, and reliability, he is dedicated to producing high-quality content that informs, educates, and inspires.


